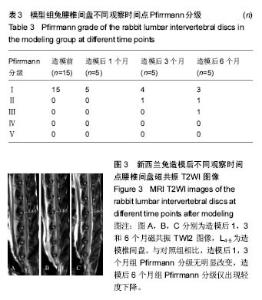
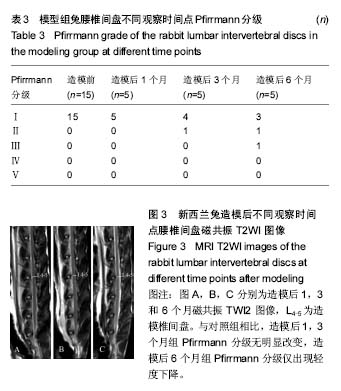
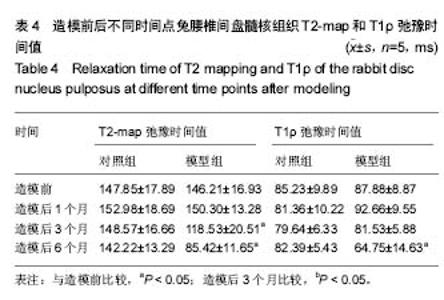
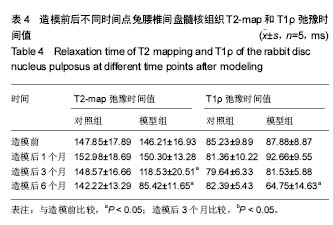
| [1] Wei F,Zhong R,Zhou Z,et al.In vivo experimental intervertebral disc degeneration induced by bleomycin in the rhesus monkey.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2014;15:340-350.[2] Masuda K, Aota Y, Muehleman C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine.2005;30(1):5-14.[3] Wei F, Zhong R, Wang L, et al. Pingyangmycin-induced in vivo lumbar disc degeneration model of rhesus monkeys. Spine.2015;40(4):E199-E210.[4] Zhou Z, Jiang B, Zhou Z, et al. Intervertebral disk degeneration: T1rho MR imaging of human and animal models. Radiology.2013;268(2):492-500.[5] 侯昌龙,杨建勇,庄文权,等. 制作兔腰椎终板下缺血模型:MRI与病理学变化验证的可行性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2010,14(2):280-284.[6] Stehling C, Luke A, Stahl R, et al. Meniscal T1rho and T2 measured with 3.0T MRI increases directly after running a marathon.Skeletal Radiol.2011;40(6):725-735.[7] Wang YX, Zhao F, Griffith J F, et al. T1rho and T2 relaxation times for lumbar disc degeneration: an in vivo comparative study at 3.0-Tesla MRI.Eur Radiol.2013;23(1):228-234.[8] 韦文姜,周智洋,郭文波,等. 兔腰椎间盘磁共振T2 mapping成像[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(35):6281-6286.[9] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见[Z]. 2006-09-30.[10] 侯昌龙,杨建勇,庄文权,等. 经皮穿刺兔腰椎椎体内注射平阳霉素对腰椎软骨终板及椎间盘的影响[J]. 中山大学学报:医学科学版,2010,31(2):221-224.[11] Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumber intervertebral disk degeneration. Spine. 2001;26(17):1873-1878.[12] Stelzeneder D, Messner A, Vlychou M, et al. Quantitative in vivo MRI evaluation of lumbar facet joints and intervertebral discs using axial T2 mapping. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(11): 2388-2395.[13] Zhang W, Ma X, Wang Y, et al. Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Spine J.2014;23(9):1830-1836.[14] Kealey S M, Aho T, Delong D, et al. Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and degenerated intervertebral lumbar disks: initial experience. Radiology. 2005;235(2): 569-574.[15] Muftuler L T, Jarman J P, Yu H J, et al. Association between intervertebral disc degeneration and endplate perfusion studied by DCE-MRI.Eur Spine J. 2015;24(4):679-685.[16] Radek M, Pacholczyk-Sienicka B, Jankowski S, et al. Assessing the correlation between the degree of disc degeneration on the Pfirrmann scale and the metabolites identified in HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;34(4):376-380.[17] Pacholczyk-Sienicka B, Radek M, Radek A, et al. Characterization of metabolites determined by means of 1H HR MAS NMR in intervertebral disc degeneration. MAGMA. 2015;28(2):173-183.[18] Keshari KR, Lotz J C, Kurhanewicz J, et al. Correlation of HR-MAS spectroscopy derived metabolite concentrations with collagen and proteoglycan levels and Thompson grade in the degenerative disc. Spine. 2005;30(23):2683-2688.[19] Zobel BB,Vadala G,Del VR,et al.T1rho magnetic resonance imaging quantification of early lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in healthy young adults. Spine. 2012;37(14): 1224-1230.[20] Wang Y X, Zhao F, Griffith J F, et al. T1rho and T2 relaxation times for lumbar disc degeneration: an in vivo comparative study at 3.0-Tesla MRI. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(1):228-234.[21] Hoppe S, Quirbach S, Mamisch TC, et al. Axial T2 mapping in intervertebral discs: a new technique for assessment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(9): 2013-2019.[22] Takashima H, Takebayashi T, Yoshimoto M, et al. Correlation between T2 relaxation time and intervertebral disk degeneration. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(2):163-167. |